‘Implementation research in nutrition’ is an emerging area of study aimed at building evidence‐based knowledge and sound theory to design and implement programs that will effectively deliver nutrition interventions. This paper describes some of the basic features of ethnography and illustrates its applications in components of the implementation process.
This study set out to assess if universal salt iodization provides sufficient dietary iodine to meet the iodine requirements and achieve adequate iodine nutrition in all vulnerable population groups.
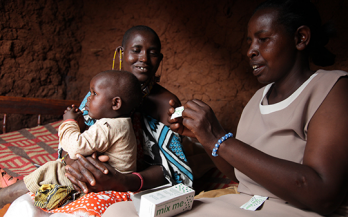
The aim of this study was to generate preliminary theories about factors affecting adherence to recommendations with regard to point-of-use fortification of foods with micronutrient powders. This study concluded that in order to achieve programs that support greater adherence, there must be an adoption of a cultural-ecological perspective to inform program design in order to address a broader set of determinants.
This study describes features of the landscape of behaviour change communication practice devoted to infant and young child feeding in low‐ and middle‐income countries by practitioners in international development organizations.
A cross-sectional survey on households with at least one child 6–23 months was conducted to update coverage figures with adequately fortified food vehicles in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, and to evaluate whether additional iron and vitamin A intake is sufficient to bear the potential to reduce micronutrient malnutrition.
This study aimed to estimate the potential contribution certain processed foods can make to micronutrient intake in Southeast Asia if they are made with fortified staples and condiments.
The objective of this study was to assess the efficiency of the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) Premix Facility in procuring quality, affordable vitamin A for fortification of edible oil in Indonesia.
The Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) was established in 2002 with a mandate to galvanize efforts by the public and private sectors to end malnutrition. This paper describes GAIN's evolution from a large-scale food fortification program focus to a broader nutrition program portfolio directed toward improving access and affordability of nutritious foods for the poor.
This paper describes the focused ethnographic study on complementary feeding that was commissioned by the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition and highlights findings from studies conducted in three very different country contexts (Ghana, South Africa and Afghanistan) burdened by high levels of malnutrition in older infants and young children.
The objective of this study was to estimate the iron and vitamin A status of preschool children (PSC) and women of reproductive age (WRA) in households consuming fortified oil and wheat flour.